What is UV radiation?
UV radiation is part of the natural energy produced by the sun. On the electromagnetic spectrum, UV light has shorter wavelengths than visible light, so your eyes can’t see UV, but your skin can feel it.
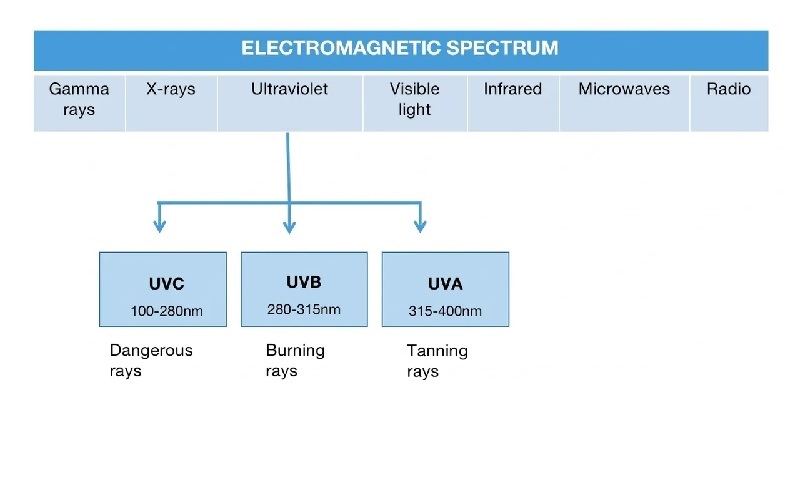
What are the different types of UV radiation?
The most common form of UV radiation is sunlight, which produces three main types of UV rays UVA, UVB & UVC
UVA rays have the longest wavelengths, followed by UVB, and UVC rays which have the shortest wavelengths. While UVA and UVB rays are transmitted through the atmosphere, all UVC and some UVB rays are absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer. So, most of the UV rays you come in contact with are UVA with a small amount of UVB.
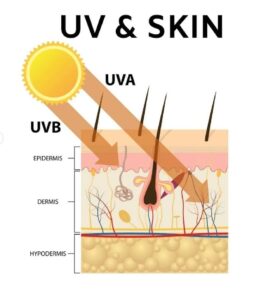
- UVA rays have a longer wavelength that can penetrate the middle layer of your skin (the dermis)
- UVB rays have a short wavelength that reaches the outer layer of your skin (the epidermis)
UVA:
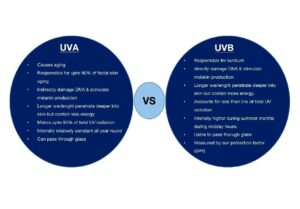
UVA rays cause tanning and shorter wavelengths of UVA also cause sunburn.
UVA is connected to the “broad-spectrum protection” you see on the labels of sunscreen products.
UVA rays, while slightly less intense than UVB, penetrate your skin more deeply. exposure causes genetic damage to cells on the innermost part of your top layer of skin, where most skin cancers occur. The skin tries to prevent further damage by darkening, resulting in a tan. over time, UVA also leads to premature aging and skin cancer.
UVA is everywhere. UVA accounts for up to 95 percent of the UV radiation reaching the earth. These rays maintain the same level of strength during daylight hours throughout the year. This means that during a lifetime, we are all exposed to a high level of UVA rays.
UVA can penetrate windows and cloud cover.
UVB:
UVB penetrates and damages the outermost layers of your skin. Overexposure causes suntan, sunburn and, in severe cases, blistering.
UVB is connected to the Sun Protection Factor (SPF) on labels of sunscreen products. The SPF number tells you how long the sun’s radiation (including some of the UVA) would take to redden your skin when using that product compared to the time without sunscreen.
UVB intensity fluctuates. While the sun’s rays are strongest and pose the highest risk late-morning to mid-afternoon from spring to fall in temperate climates and even greater timespans in tropical climates, UVB rays can damage your skin year-round, especially at high altitudes or on reflective surfaces like snow or ice.
UVB rays can be filtered and do not penetrate glass.
Benefits of UV radiation:
Exposure to UVB radiation helps the skin produce a type of vitamin D (vitamin D3), which plays an important role – along with calcium – in bone and muscle health
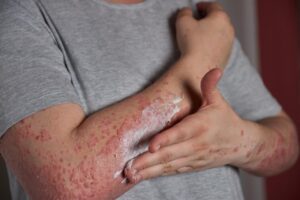
UV radiation, in the form of lasers, lamps, or a combination of these devices and topical medications that increase UV sensitivity, are sometimes used to treat patients with certain diseases like Rickets, Psoriasis, Eczema, Vitiligo.
Protect yourself!
Despite the risk factors, you can safely, happily enjoy the great outdoors by protecting your skin against UV exposure with broad-spectrum sunscreen and sun-safe clothing, hats and eyewear. You can also consider UV window film for your home and car.